WHAT IS CBD?
Cannabidiol, also known as CBD, is a naturally occurring chemical compound derived from the Cannabis Hemp plant. CBD is a phytocannabinoid that was discovered in 1940. It is one of some 113 identified cannabinoids which are unique to Cannabis and endow the plant with its robust therapeutic profile.
CBD is extracted from the leaves and flowers of the Hemp Plant, and once it’s isolated from the rest of the plant, it can be incorporated into a plethora of products, from sublingual oils, to topical lotions, soft gels, capsules, and gummies.
While CBD’s therapeutic effects are still being clinically evaluated, there is much anecdotal evidence to suggest that CBD is safe, effective and has many medicinal benefits. CBD is “nonpsychoactive” which mean it does not produce a “high.” CBD does not increase appetite or produce withdrawal symptoms, and it is not addictive.
What is the Science behind CBD?
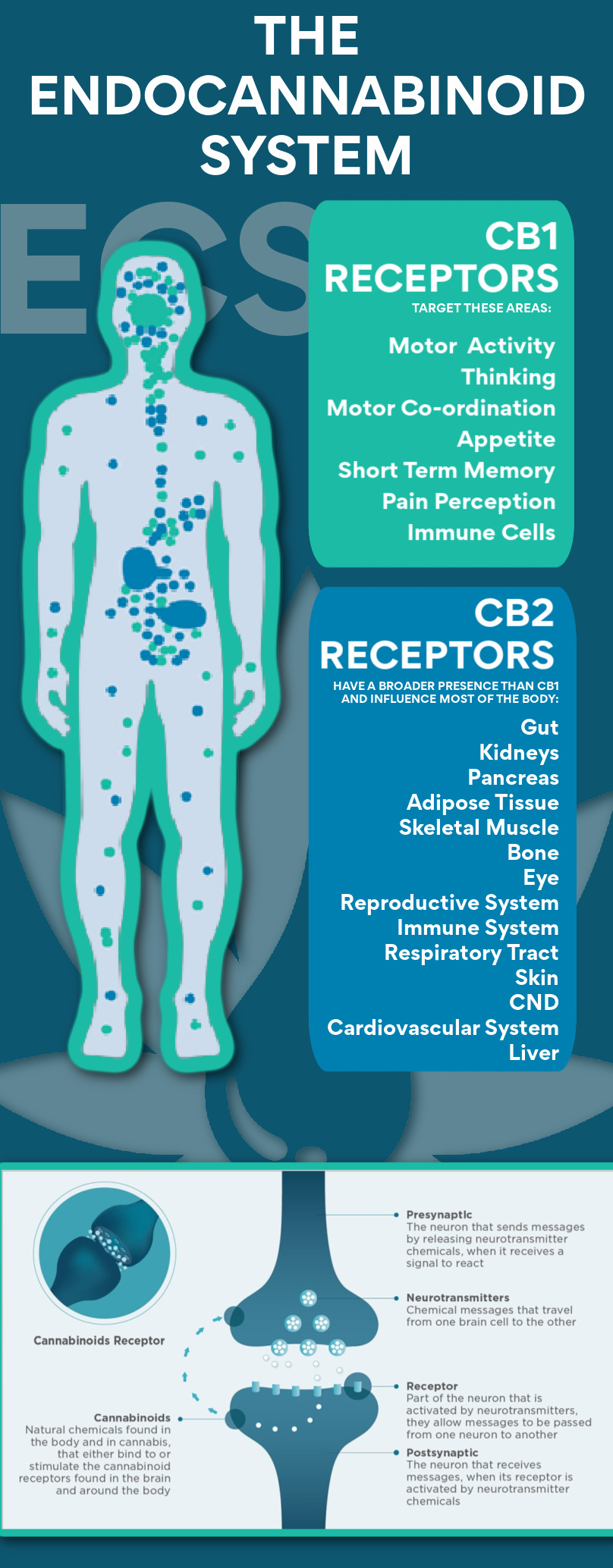
The human body is home to a complex physiological and biological system known as the Endocannabinoid System ( ECS). ECS is a sub-system within our central nervous, peripheral nervous, and immune systems that maintains homeostasis in the body, creating the ideal conditions for cells to perform optimally. The ECS system consists of naturally-produced cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors and regulates a number of physiological and cognitive processes that affect our everyday experience, such as pain sensation, sleep, appetite, mood, hunger, memory, body temperature, intestinal fortitude, immune activity, and blood pressure. The Endocannabinoid System plays a vital role in regulation of our bodies in many ways and it appears one of its primary functions is to keep us in a place of homeostasis Thus, it stands to reason that dysfunction of the endocannabinoid system or homeostasis would lead to disease.
The ECS comprises a variety of receptors that trigger physiological reactions, thereby inducing the various effects of cannabinoids. Cannabinoids bind endogenous cannabinoid receptors found throughout our bodies, which are mainly the two G protein-coupled receptors: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are found in the central and peripheral nervous system and influence appetite, mood, and pain. CB2 receptors are found on immune cells and regulate cytokine production and inflammation. Those receptors are expressed by both osteoblasts and osteoclasts. CBD interacts directly and indirectly with the various receptors to produce its therapeutic effects. CBD works as an immunostimulator by igniting the Endocannabinoid System and helping it to become more efficient. Interestingly, CBD also shows affinity for binding noncannabinoid receptors, including the dopamine, serotonin, and opioid receptors.
There are a number of ways in which CBD interacts with our bodies. One of the primary ways is by mimicking the effects of similar compounds in our bodies ( Endocannabinoids ). They got that name because of their similarities to the compounds found in the cannabis plant. Endocannabinoids are part of the Endocannabinoid System which has many functions in our bodies and its discovery has changed the way we view our health and disease.
CBD research is in its infancy and we are excited about the possibilities for this natural remedy. As more research is performed and reported, our page will be updated with the most recent information
The adjacent image shows the multiple areas of our body were the Endocannabinoid System resides.

What is the Difference between Full Spectrum, Broad Spectrum, and Isolate CBD Oil?
Understanding the difference between the three major types of CBD products ( Full spectrum vs Broad Spectrum vs Isolate CBD oil ) is one of the most important first steps on your CBD journey. Once you understand the difference between them, you’ll be better equipped to make an educated decision on which CBD oil product to buy for your needs.
The three most popular types of CBD oil used today are: Full Spectrum, Broad Spectrum and Isolate. You may also come across products labeled as “Whole Plant” or “Pure CBD.” This article will explain the differences and similarities among these.
Full Spectrum
Full spectrum (or “whole plant”) products contain CBD as well as terpenes and other cannabinoids such as CBG, CBN and trace amounts of THC. Usually these will be in ratios that were naturally-occurring and extracted from the plant and specific strain. Terpenes and cannabinoids are occasionally added back into products as an isolated form to raise the potency of the product.
Those subject to drug testing should be cautious when it comes to full spectrum products. The THC found in full spectrum hemp oil products is minimal (less than 0.3%), but can still trigger a positive drug test.
Broad Spectrum
Broad spectrum products contain an array of cannabinoids and terpenes like Full Spectrum but contains “Non Detectable” THC based on the manufacturer’s Certificate of Authenticity (COA) lab report. Even though a lab report may state “No Detectable” THC, there still may trace amounts of THC but is negligible and is nowhere near the amount usually found in full spectrum products, and will not show up in a Drug Screen. Reputable companies use an unbiased accredited Third party lab reports that can tell you which cannabinoids and terpenes are in the product and at what levels.
These products have often gone through additional processing to try to isolate and remove as much THC as possible while still maintaining the other cannabinoids and terpenes. In other cases, they are isolate-based with additional cannabinoids and terpenes added in. Broad Spectrum is the CBD oil product of choice for those who get drug tested or are sensitive to other cannabinoids such as THC
Isolate
Products labeled as isolates will generally be highlighted as being 99+% “pure CBD.” Usually, these products will have nothing but CBD in them because the CBD has literally been isolated from everything else. You will not get the other important Cannabinoids such as CBG, CBC, and CBN, therefore you may not get the robust therapeutic and medicinal benefits like you would with a Full Spectrum and Broad Spectrum CDB products.
What is the Optimal Dosage for CBD?
There is very little information about the absorption and bioavailability of CBD. Every person will be having a different therapeutic affect based on the amount of CBD they take. The “Rule of Thumb” when taking CBD is to “Start Slow and Start Small”. An effective dosage can range from as little as a few milligrams of CBD-enriched cannabis oil to a gram or more. Begin with a small dose of CBD oil, especially if you have little or no experience with CBD. Take a few small doses over the course of the day rather than one big dose. Use the same dose and ratio for several days. Observe the effects and if necessary adjust the ratio or amount. Don’t overdo it. Cannabis compounds have biphasic properties, which mean that low and high doses of the same substance can produce opposite effect. CBD has no known adverse side effects, but an excessive amount of CBD could be less effective therapeutically than a moderate dose. “Less is more” is often the case when taking CBD products.